🤩Public Rollouts of Chinese ChatGPT Rivals; China's First Text-to-Image Lawsuit; HD Text-to-Video Model
Weekly China AI News from August 28 to September 3
Hello all! In this issue I will discuss public rollouts of Chinese chatbots. Over 170,000 people have tuned in for a livestream on text-to-image lawsuits. Meet VideoGen, a new model for generating high-definition videos from text prompts
Chinese ChatGPT Rivals Receive Green Light for Public Rollouts
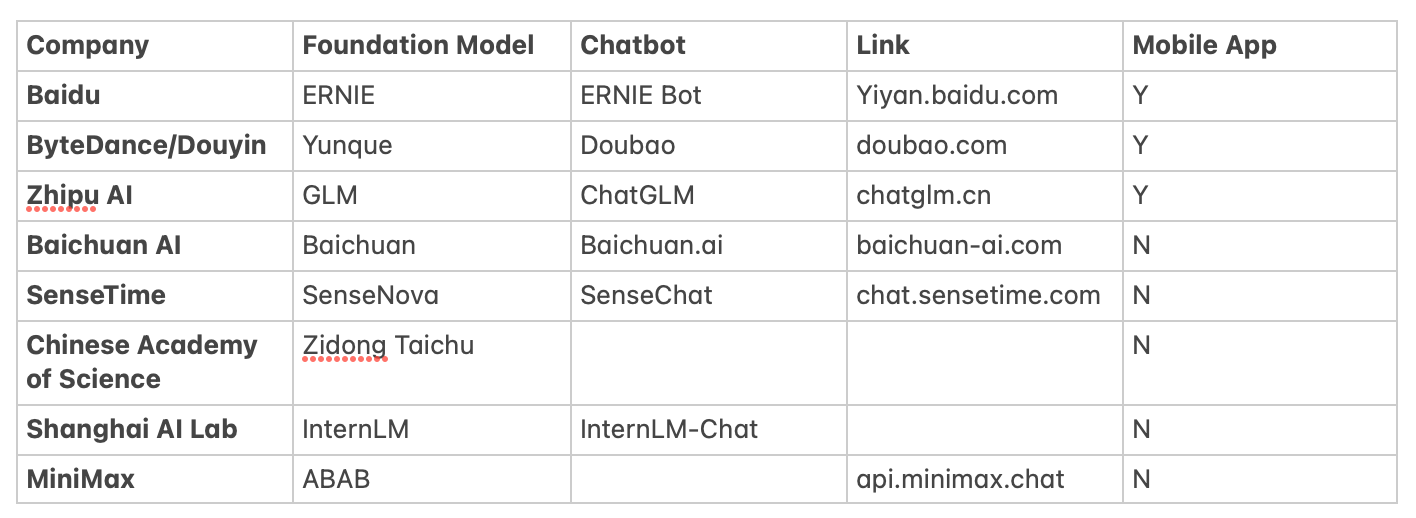
What’s new: At the stroke of midnight on August 31, a new era dawned for China’s large language models (LLMs). Just two minutes into the new day, Baidu first announced the public rollout of its long-awaited conversational AI bot, ERNIE Bot. Within the next two hours, Zhipu AI—a Meituan-backed startup—and Baichuan AI, founded by Sogou Co-founder Wang Xiaochuan, also released their own ChatGPT-like chatbots.
According to Chinese media reports, the first group of eight LLMs has cleared the regulatory filings set forth by the Interim Measures for the Management of Generative Artificial Intelligence Services, effective August 15. The regulation requires generative AI service providers “having public opinion attributes or social mobilization capabilities” to complete algorithm filings. These models are now authorized for public use starting August 31, although Chinese regulators haven’t issued an official statement.
However, not all launches went smoothly: SenseChat seemed to become unavailable shortly after its debut.
Meanwhile, iFlytek and Alibaba Cloud have also filed regulatory approvals for their respective chatbots, Spark and Tongyi Qianwen, as stated in their official announcements. (At the time of writing, on September 5, iFlytek, 360, and WPS have announced that their chatbots or LLMs are publicly accessible.)
Day one spotlight: On its first day, Baidu’s ERNIE Bot stole the limelight, attracting 1 million users within just 19 hours and answering over 33 million questions in its first 24 hours. A Baidu representative disclosed that the company is speeding up development to release its next-generation foundation model as early as possible.
Unique features of Chinese chatbots: Chinese chatbots offer functionalities that extend beyond those of their U.S. counterparts like ChatGPT and Claude. For example, ERNIE Bot not only understands and generates text but can also interpret images and audio. It further offers data visualization tools and video generation. The mobile version features a community section where users can explore trending prompts and create similar content.
ByteDance’s Doubao, meanwhile, provides multiple chatbots with diverse personalities to cater to varying user needs. Both ERNIE Bot and ChatGLM also offer pre-defined prompts to assist with business writing and social media posts.
170,000 Viewers Watch Livestream on Text-to-Image Lawsuits
What’s new: On August 24, the Beijing Internet Court, a specialized court that handles Internet cases, publicly heard a case involving the copyright of AI-generated images, the first of its kind in China.
The plaintiff, Li, used Stable Diffusion to generate a character image. This image was then posted on social media (Little Red Book) at the end of February.
The defendant, Liu, a poetry blogger, used the same image as an illustration for an article posted on his another Medium-like account (Baijiahao) in March. Liu removed the watermark that can indicate the image’s origin.
Li is suing Liu for infringement of the right to attribution and the right to information network dissemination. He is seeking RMB 5,000, in damages and a formal apology.
Why it matters: This case has garnered significant attention, with the proceedings live-streamed on multiple platforms, including Douyin and Kuaishou. The live-stream attracted over 170,000 online viewers. The questions raised during the court proceedings include: Does the image in question qualify as a copyrighted work? If so, does the plaintiff hold the copyright? Did the defendant’s actions violate the right to attribution and the right to information network dissemination? What responsibilities should the defendant bear if found guilty?
The case has yet to reach a verdict and is still under review.
Weekly News Roundup
🌟 Weibo launched an AI chat feature that mimics celebrity chat styles. Once the user grants permission, the AI assistant will engage in automatic replies, enhancing user experience with emotional companionship.
🏥 Fudan University unveiled a personal assistant for healthcare and open-sourced a dataset of 470,000 high-quality entries.
🤖 On September 1st, Xiaomi applied for multiple trademarks including “Xiaomi Large Model” and “MiLM-6B”. The newly updated Xiaoai assistant now features generative models and supports intelligent Q&A, copywriting, and even image creation.
📜 Tongfang Knowledge Network has signed an innovation lab collaboration agreement with Huawei Cloud. The partnership aims to develop AI models for knowledge services based on Huawei’s Cloud Pangu model.
📊 The CAC revealed announced the completion of the second round of registrations for deep synthesis algorithms. The list features 110 algorithms from major industry players such as Huawei, Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent, JD.com, 360, iFlytek, SenseTime, and more.
Trending Research
Introducing VideoGen, a cutting-edge method for generating high-definition videos from text prompts. By first creating a high-quality reference image from the text, the system then uses a novel technique called “latent diffusion” to produce a video with consistent and high-quality frames. This approach sets a new standard in the field of text-to-video generation, offering improved visual fidelity and temporal resolution.
Paper: VideoGen: A Reference-Guided Latent Diffusion Approach for High Definition Text-to-Video Generation
Affiliations: Department of Computer Vision Technology (VIS), Baidu
Researchers have developed a new multimodal model called LLaSM, which goes beyond just understanding text and images—it can understand and respond to spoken instructions as well. This makes human interaction with AI more natural and convenient. The team also released a dataset to help further research in this emerging field.
Affiliations: LinkSoul.AI; Peking University; 01.ai (founded by Kai-fu Lee)
Code and demo: https://github.com/LinkSoul-AI/LLaSM and https:// huggingface.co/spaces/LinkSoul/LLaSM
Dataset: https://huggingface.co/datasets/LinkSoul/LLaSM-Audio-Instructions
A new study reveals that mastering one programming language can make it easier to learn others, especially when fine-tuning AI models designed to understand code. Researchers tested eight popular languages like Python, Java, and HTML on a platform called StarCoder. They found that training the AI in one language significantly improved its performance in others. For instance, an AI trained in Python boosted its Java skills by nearly 18%.
Paper: Can Programming Languages Boost Each Other via Instruction Tuning?
Affiliations: Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Science; Peking University; Huawei
Dataset: https://github.com/NL2Code/CodeM
A new comprehensive survey examines the rise of autonomous agents powered by LLMs. The survey proposes a unified framework to understand various LLM-based agent architectures and their applications in fields like social science and engineering. It also highlights evaluation methods and future challenges in this rapidly evolving field.
Paper: A Survey on Large Language Model based Autonomous Agents
Affiliations: Gaoling School of Artificial Intelligence, Renmin University of China
Repo: https://github.com/Paitesanshi/LLM-Agent-Survey