Microsoft Chatbot Spinoff Launches ‘Metaverse’ App with AI Interaction; Starch Synthesis from CO2; Talk-to-Edit Your Face
China’s AI news in the week of September 26, 2021
XiaoIce Launches XiaoIce Island, A Virtual “WeChat” with AI Avatars
Xiaoice, a Chinese chatbot upstart spin-off from Microsoft a year ago, introduced a virtual social media app, dubbed Xiaoice Island, to the public where users can interact with their self-developed AI avatars. Boasted as the world’s first social media platform for human-AI interactions, the beta version of Xiaoice Island is now available for iOS and Android users through TestFlight.
Users will enjoy a similar interface of WeChat or Line to send messages and share social media posts with connected friends. However, instead of communicating with real humans, users will customize up to 10 AI beings - appearances, voices, personalities, and abilities - and live a virtual life with them like Animal Crossing. These AI beings are not puppies, but human-like companions, assistants, and creators that are able to generate short/long-form videos, music, articles, and other content that are protected under intellectual properties, said the company.
Xiaoice, which recently raised a new funding round that pushes its market value to $1 billion, has been touting the emotional intelligence of its underlying AI companion technology. In addition to a well-designed dialogue manager and core chat skills, the company also added a dedicated emotional computing module that can help the AI agent recognize human feelings and states and respond throughout long conversations. The Xiaoice AI system has been built in 1 billion devices.
Xiaoice’s latest launch is riding on the recent wave of Metaverse, the futuristic immerse world Facebook and Apple are doubling down on to potentially replace mobile phones. While Xiaoice Island doesn’t offer a VR experience, it features all characteristics of a Metaverse concept - community, self-evolving, and immersiveness.
This is a big week for Chinese conversational AI as Baidu also released a large-scale Chinese chatbot system PLATO-XL. The model has up to 11 billion parameters and obtains state-of-the-art results across multiple dialogue benchmarks.
Science: Artificial Starch Synthesis From Carbon Dioxide (CO2) for the First Time
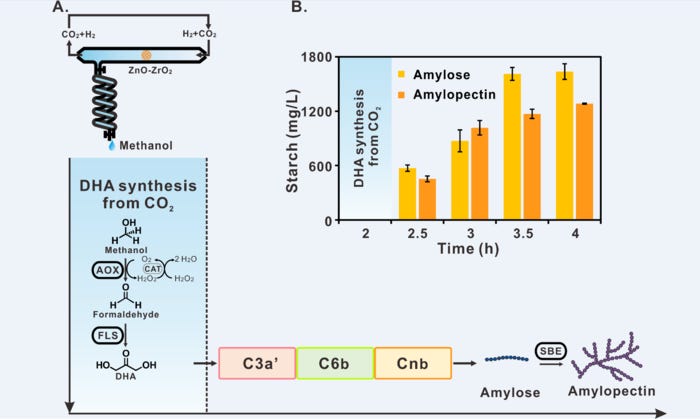
This is not exactly AI news, but a pretty big bombshell in the Chinese scientific community that didn’t make a splash globally. Simply speaking, a team of Chinese scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences has successfully synthesized artificial starch from carbon dioxide (CO2), meaning my exhaled CO2 might contribute to the production of my food. The research has been published in Science.
This new CO2-to-starch synthesis will kill two birds with one stone - reducing carbon emissions to overcome climate change and resolving food crisis.
According to the press release, “scientists at the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology (TIB) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) designed a chemoenzymatic system as well as an artificial starch anabolic route consisting of only 11 core reactions to convert CO2 into starch.”
The scientists said the technology would open a window for industrial manufacturing of starch from CO2, but the cost is much higher than agricultural planting. So the timeline of deploying such technology into industrial production remains unknown.
Edit Your Selfie by Talking
Have you ever encountered a situation where you know how to perfect your selfie — a bigger smile and maybe higher cheeks — but are bad at execution? Well, recent research on AI-enabled facial editing allows you to edit your face by only talking.
In the paper Talk-to-Edit: Fine-Grained Facial Editing via Dialog, researchers from Nanyang Technological University and the Chinese University of Hong Kong proposed an interactive facial editing framework that performs fine-grained attribute manipulation through dialog between the user and the system.
The Talk-to-Edit system first interprets users’ language requests, i.e darken my facial color, into machine-readable signals, which then guide the system to change the target attributes of the picture. The system then returns an edited picture along with feedbacks. The process will keep going until the user is satisfied with the result.
The main contributions in the research include a proposed location-specific semantic field to achieve more continuous and fine-grained facial editing and a large-scale visual-language dataset CelebA-Dialog that encompasses fine-grained attribute labels and corresponding textual descriptions.
Experiments show 80% of users are in favor of the system by its smoothness, identity/attribute preservation, and visual photorealism, and dialog fluency. You can find more details on the project page: https://www.mmlab-ntu.com/project/talkedit/.
Investment News:
Momenta, a Suzhou-based autonomous driving company specialized in advanced driver assistance system features, raised $300 million from General Motors to accelerate the development of next-generation self-driving technologies for future GM vehicles in China. The massive funding lifts its total funding to more than $1 billion.
Black Sesame Technologies, a self-driving chip startup, raised "hundreds of millions of dollars" from Xiaomi’s industry investment fund and other investors. Founded in 2016, the Shanghai-headquartered company develops image processing, perception algorithms, and SoC designs for autonomous vehicles.
Advance Intelligence Group, a Singapore-headquartered AI-driven technology company, has closed its $400 million Series D round financing from an investor consortium led by SoftBank Vision Fund 2 and Warburg Pincus. Founded in 2016, the Group has built an ecosystem of AI-powered, credit-enabled products, and services across twelve markets.