Masked Image Modeling; JD.com AI Chief Departs; Baidu to Expand Robotaxi in 100 Cities
China’s AI news in the week of November 21, 2021
ByteDance Introduces iBOT for Masked Image Modeling
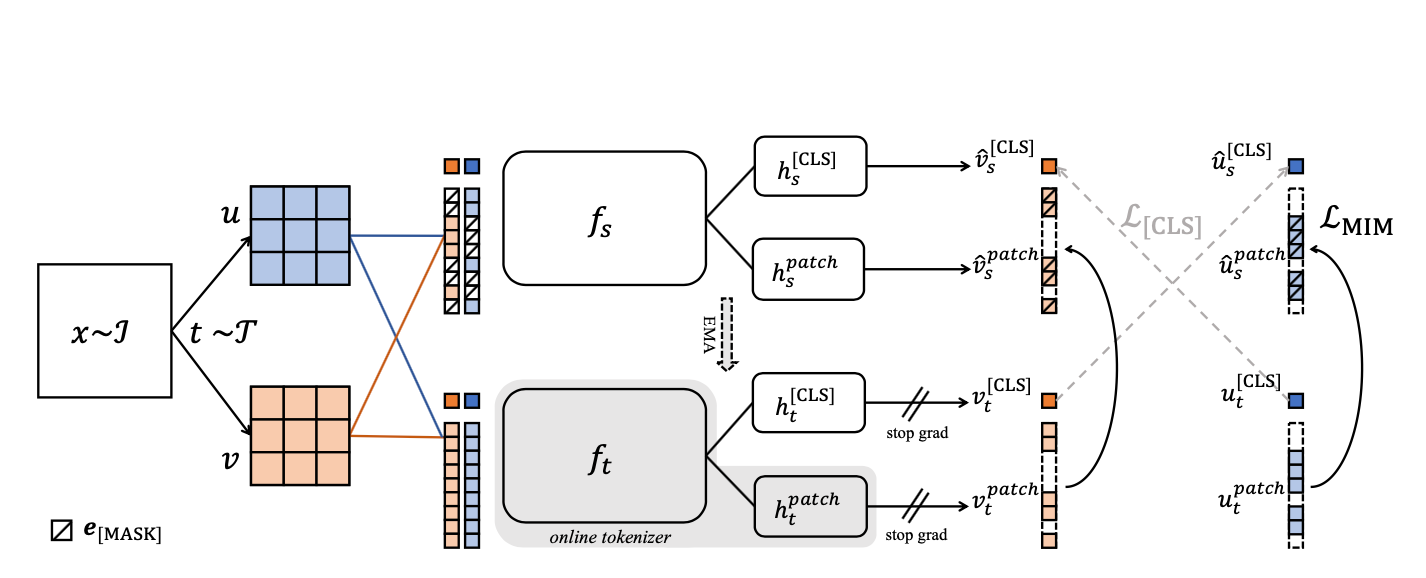
Inspired by the success of Transformers in pre-trained language models, a recent paper from ByteDance, John Hopkins University, Shanghai Jiaotong University and UC Santa Cruz studied masked image modeling (MIM) in computer vision. They proposed a new framework that can perform masked image modeling (MIM) with a visual tokenizer.
In the paper iBOT: Image BERT Pre-Training with Online Tokenizer, researchers formulated the MIM as knowledge distillation (KD), which learns to distill knowledge from the tokenizer, and further proposed to perform self-distillation for MIM with the help of twin teacher as online tokenizer. The target network is fed with a masked image while the online tokenizer with the original image. The goal is to let the target network recover each masked patch token to its corresponding tokenizer output.
iBOT advances ImageNet-1K classification benchmark under k-NN, linear probing and fine-tuning protocols to 77.1%, 79.5%, 83.8% with ViT-Base/16 respectively, which is 1.0%, 1.3%, 0.2% higher than previous best results. When pre-trained with ImageNet-22K, iBOT with ViT-L/16 achieves a linear probing accuracy of 81.6% and a fine-tuning accuracy of 86.3%, both 0.3% higher than previous best results. Beyond that, the advancement is also valid when transferring to other datasets or under semi-supervised and unsupervised classification settings.
Moving forward, researchers plan to scale up iBOT to a larger dataset (e.g., ImageNet-22K) or larger model size (e.g., ViT-L/16 and ViT-H/16) and investigate whether MIM can help Vision Transformers more scalable to unlabelled data in the wild.
The paper echoes another recent research from Facebook AI Research, Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners, which masks random patches of the input image and reconstructs the missing pixels. The experiment showed that the model achieves the best accuracy (87.8%) among methods that use only ImageNet-1K data.
JD.com AI Chief Departs to Start New Company
Following the departure of former Ant Group Chief AI Scientist Alan Qi Yuan two weeks ago, Chinese e-commerce giant JD.com also lost its President of JD Cloud & AI and Chair of JD Technology Committee, Dr. Bowen Zhou. Chinese media reported that Dr. Zhou will start a new company specialized in AI.
Before he joined JD.com in October 2017, Dr. Zhou held several key leadership positions during his 15-year tenure at IBM's headquarter in New York, most recently serving as Director of the AI Foundations Lab at IBM Research, Chief Scientist of IBM Watson Group, and a Distinguished Engineer of IBM. An IEEE Fellow, Dr. Zhou publishes extensively and his main research areas span natural language processing,machine learning and other core AI fields. Dr. Zhou received a Ph.D. in Electrical & Computer Engineering from the University of Colorado at Boulder, and a Bachelor's degree from the University of Science & Technology of China.
Dr. Zhou laid the AI foundation for JD.com by establishing the JD AI Research Institute and NeuHub, JD.com’s open AI platform.
Baidu Will Launch Robotaxi Services in 100 Cities by 2030, CEO Says
Baidu’s robotaxi platform Apollo Go has delivered 115,000 rides in the third quarter of 2021, Baidu CEO Robin Li told investors in a quarterly earnings call. In comparison, the world’s robotaxi leader Waymo was doing 1,000 to 2,000 rides every week by early 2020, The Verge reported. Waymo hasn’t updated its stats since then.
Mr. Li said the scaled offering of Apollo Go makes Baidu “the largest robotaxi service provider in the world”. Apollo Go now operates in five Chinese cities - Beijing, Guangzhou, Changsha, Cangzhou, and Shanghai - where passengers can hail a robotaxi using the mobile platform. Still, most robotaxis are paired with safety drivers to abide by local regulations. Baidu has been testing driverless vehicles since 2020.
Baidu aims to expand its Apollo Go service to 65 cities by 2025 and 100 cities by 2030, Mr. Li added.
According to Baidu’s earnings report, Baidu Apollo has accumulated over 10 million L4 test miles, up 189% year over year, and has received 411 autonomous driving permits, reflecting Apollo's broad geographic coverage and wide-ranging test scenarios, according to the earnings. Rides provided by Apollo Go doubled sequentially. As of September 2021, the Apollo platform has over 210 partners, 55,000 global developers, and 700,000 lines of open-source code.
Baidu is also ramping up its efforts to revamp transportation, reducing traffic congestion in short term and constructing the road infrastructure that is tailored for autonomous vehicles in the future. Baidu's ACE smart transportation solution has been adopted by 24 cities, tripling year over year, based on a contract amount of over RMB 10 million.
Investment News:
MAXIEYE, a Shanghai-based autonomous driving developer, has raised CN¥300 million ($47 million) in its Series B funding round led by Huizhou Desay SV Automotive. Founded in 2016, the company provides pre-installed driver assistance and advanced self-driving capabilities for passenger vehicles.
Startdt, an Hangzhou-based big data and AI solution provider, has announced its Series C+ funding round worth CN¥200 million ($31.3 million). Founded in 2016, the company specializes in developing AI-driven IoT hardware and data management platforms that utilize AI facial recognition and person re-identification technology to collect and analyze consumer behaviors data, providing effective data solutions for retail vendors and government agencies to better understand the consumer base.
Truck.Tech, a Beijing-based autonomous truck startup, has raised a CN¥multi-hundred million funding round jointly led by Yuexiu Industrial Fund, Zhongwei Capital, Bohai Zhongsheng. Founded in 2017, the company develops SAE Level 4 driverless trucks, based on its home-grown driverless hardware and software systems as well as Velodyne LiDARs.