🤺 China's AI Model Battle; MOSS Open-Sourced; Reinforcement Learning in Minecraft AI
Weekly China AI News from April 17 to April 23
Dear readers, this week we will discuss China’s competitive AI landscape. Fudan University has open sourced its ChatGPT-like LLM, MOSS. Peking University and BAAI have developed a multi-task agent in Minecraft utilizing reinforcement learning (RL). Also, do you know that 63% of Chinese developers have never made money from open source projects?
China Ignites a Hundred-Model-Battle
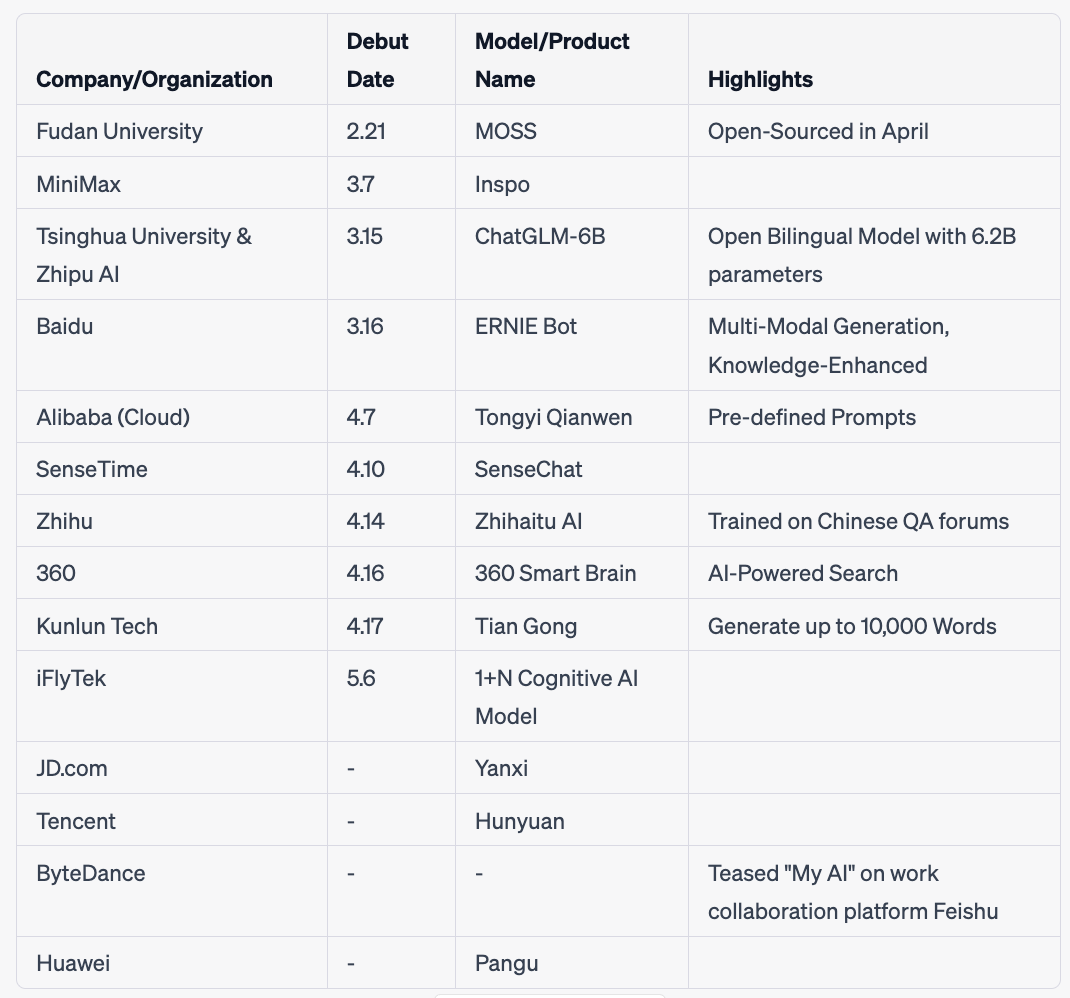
What’s new: Over 30 ChatGPT-like large language models (LLMs) have emerged in the Chinese market, as reported by a local media outlet, signaling the start of a competitive AI landscape in the country. This fierce competition has been dubbed the “Hundred-Model-Battle” (百模大战). Here is a brief timeline:
On April 18, six announcements related to LLMs were made.
DingTalk announces the official integration of Alibaba’s Tongyi Qianwen.
Baidu’s ERNIE Bot has been fully applied to its internal intelligent work platform Infoflow.
ByteDance’s cloud service Volcano Engine releases its self-developed DPU (Data Processing Unit) chip, as well as a training cloud platform for LLMs.
Kingsoft Office announces the launch of WPS AI, similar to Microsoft’s Copilot product, powered by MiniMax.
APUS launches its self-developed, multi-modal 100-billion-parameter LLM AiLMe.
At the Auto Shanghai Show, Banma Zhixing announced the integration of the Tongyi Qianwen, with IM Motors becoming the first onboard brand.
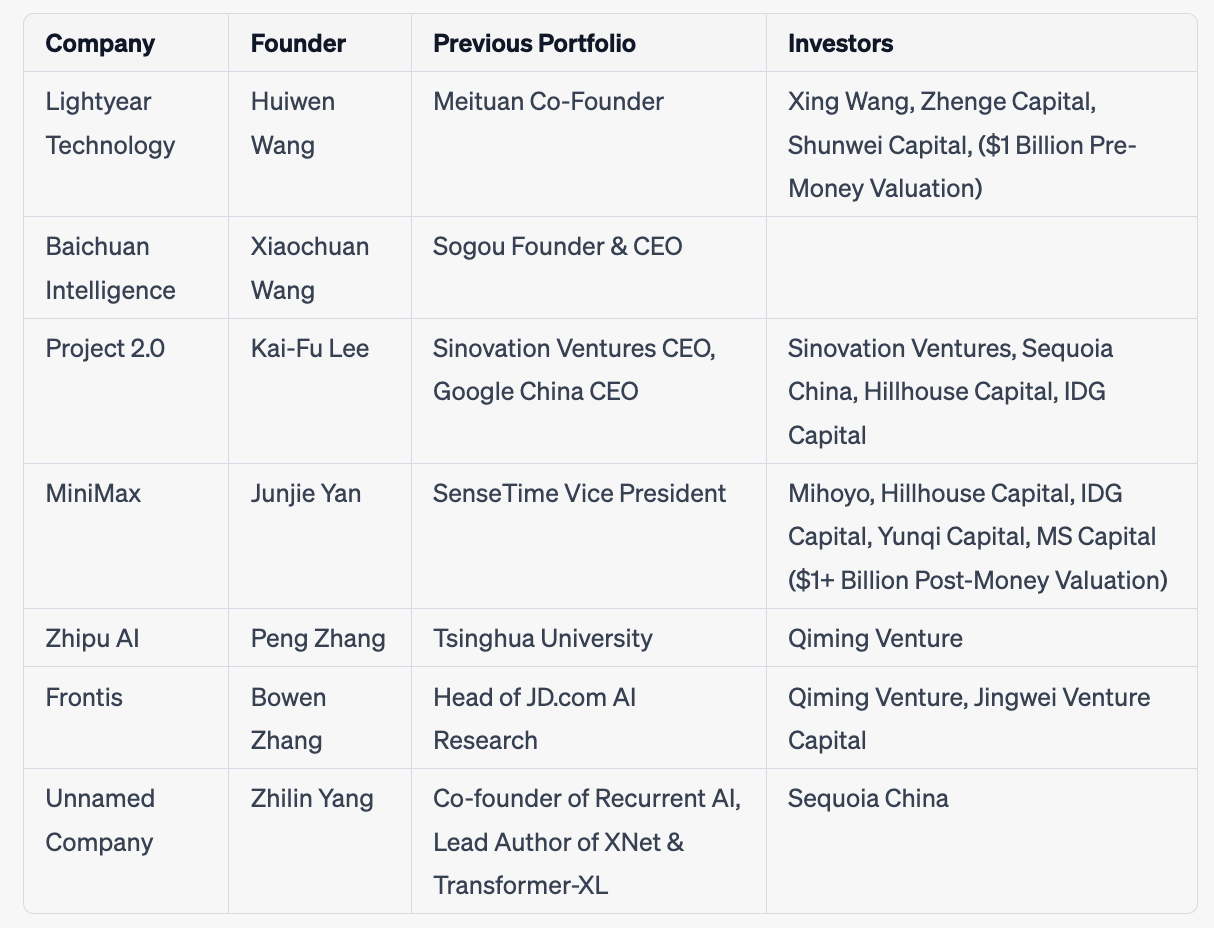
Chinese rockstar entrepreneurs are assembling their teams to develop a Chinese version of ChatGPT and eventually advance to general AI. According to The Information, American investors are supporting major Chinese venture capital firms actively involved in local AI startup deals.
Quick takeaways:
There is no clear winner in the Chinese ChatGPT race, although Baidu’s ERNIE Bot currently holds a leading position.
Venture capitalists generally believe that the window for startups in LLMs has largely closed, with the first round of capital competition coming to an end.
Fudan University Open Sources ChatGPT-Like MOSS with Plugins
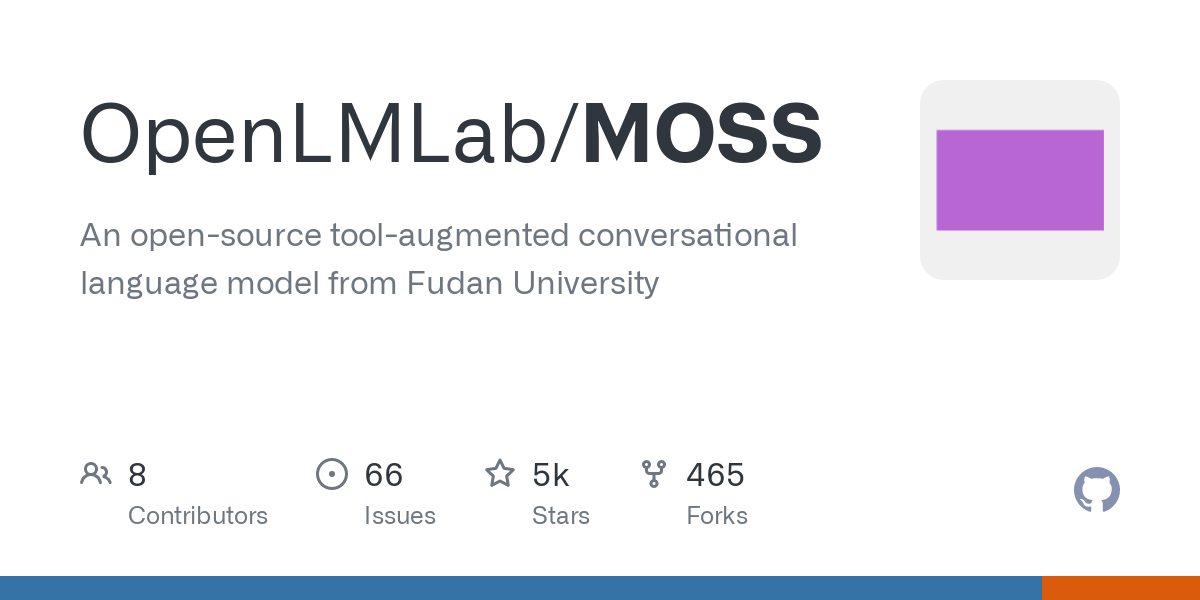
What’s new: Fudan University’s NLP Lab has open-sourced its widely-anticipated MOSS, claiming it as China’s first open-source conversational LLM with plugins. MOSS, which made debut in February, is capable of tasks such as dialogue generation, programming, and factual question-answering. Read more at previous Recode China AI issue.
Why It Matters: Said Prof. Qiu Xipeng, head of the MOSS project, the focus for the next generation of large language models (LLMs) is to align with the real world and human values, becoming a true intelligent agent. MOSS’s open-source nature is expected to enable collaboration and innovation in the research community.
16 Billion: The MOSS model, including its source code, data, and model parameters, is now available on platforms like Github and HuggingFace. More details:
Four MOSS models have been open sourced, including the base model, MOSS-003, which boasts 16 billion parameters. It has been trained on high-quality Chinese and English corpora, comprising approximately 700 billion tokens, including 100 billion tokens from Chinese data and 300 billion tokens from code data.
Four multi-turn dialogue datasets will also be released. Among them is a dataset containing 1.1 million dialogues based on around 100,000 user inputs collected during the MOSS-002 beta phase and generated using GPT-3.5.
The MOSS models can run on a single A100/A800 or two 3090 GPUs at FP16 precision, and on a single 3090 GPU at INT4/8 precision.
Plugins: Following OpenAI’s announcement last month to introduce Plugins, a powerful tool enabling ChatGPT to access up-to-date information, perform computations, and utilize third-party services, MOSS has also adopted a similar approach. They have added a dataset of plugin-enhanced multi-turn dialogue data, which includes 300,000 multi-turn dialogues that support four plugins: search engines, text-to-image, calculators, and equation solvers. This dataset is set to be open-sourced soon.
Chinese Developers Call for Open-Sourcing of ChatGPT
What’s new: “2022-2023 China Open Source Developer Survey Report”, conducted by Chinese developer communities and media outlets, provides an accurate representation of Chinese open-source development.
The report revealed some interesting findings:
Only 2% of Chinese developers never used open source software, and 49% of developers have participated in open source projects.
In the past two years, companies have become more aware of open source compliance, setting up Open Source Program Offices (OSPO), but more than 53% of developers have never heard of them. In addition, 21.4% of developers have not paid attention to open source licenses when using open source projects, and developer awareness of open source risks still needs to be strengthened.
63% of developers have never made money from open source projects, and over 80% of open source developers rely on their passion to drive their projects, hoping that the industry can find better solutions soon.
9.4% of developers believe that there is no need to establish a Chinese open source foundation, as there are already many mature foundations abroad.
Open source AI remains the most popular technology field for developers this year, and open sourcing the highly anticipated ChatGPT remains a hot topic.
Weekly News Roundup
📆 Alibaba’s DingTalk integrates Tongyi Qianwen, kicking off the transformation of AI for productivity tools, President Jun Ye said.
🚙 Huawei released the AITO M5 Smart Drive Edition, equipped with both Huawei’s ADS 2.0 Advanced Intelligent Driving System and HarmonyOS Intelligent Cockpit 3.0.
📲 Xiaomi CEO Jun Lei said Xiaomi has been working in the AI field for many years. Xiaomi is currently developing some interesting technologies and products in LLMs.
📡 The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology said that they will promote key core technologies such as 6G, optical communication, and quantum communication to accelerate breakthroughs, and increase research and development efforts in cutting-edge technologies such as AI, blockchain, and digital twins.
✍🏻 Starting in Q2, Weibo will test the Generative AI Content Creation Assistant to help popular users create content.
Trending Research
Plan4MC: Skill Reinforcement Learning and Planning for Open-World Minecraft Tasks
Affiliations: Peking University, BAAI
The study focuses on building a multi-task agent in Minecraft using reinforcement learning (RL). To improve sample efficiency, the process is divided into learning basic skills and planning over those skills. Three types of fine-grained basic skills are proposed, using RL and intrinsic rewards. Large Language Models are used for skill planning by creating a skill graph. A skill search algorithm generates suitable skill plans while solving tasks. The method outperforms baselines in 24 diverse Minecraft tasks, requiring the sequential execution of over 10 skills. Project resources are available online.
UltraChat: Large-scale, Informative, and Diverse Multi-round Dialogue Data
Affiliations: Tsinghua University
This project aims to construct open-source, large-scale, and multi-round dialogue data powered by Turbo APIs to facilitate the construction of powerful language models with general conversational capability. In consideration of factors such as safeguarding privacy, we do not directly use any data available on the Internet as prompts. To ensure generation quality, two separate ChatGPT Turbo APIs are adopted in generation, where one plays the role of the user to generate queries and the other generates the response. We instruct the user model with carefully designed prompts to mimic human user behavior and call the two APIs iteratively.
Inpaint Anything: Segment Anything Meets Image Inpainting
Affiliations: University of Science and Technology of China, Eastern Institute for Advanced Study
Inpaint Anything (IA) is a mask-free image inpainting approach based on the Segment-Anything Model (SAM). It offers a user-friendly pipeline with three main features: Remove Anything, Fill Anything, and Replace Anything. This new paradigm aims to address challenges in mask selection and hole filling in modern image inpainting systems.