China Demonstrates Quantum Supremacy; VOLO Tops ImageNet; Uncrewed Excavator
China’s AI news in the week of June 28, 2021
Please subscribe here to support Recode China AI.
Better than Google? Chinese scientists demonstrate Quantum Supremacy
A Chinese research team led by Dr. Jianwei Pan, also known as “the godfather of China’s quantum”, recently said they achieved quantum advantage in a task where the computational cost of the classical simulation is 2-3 orders of magnitude higher than Google’s work in Nature, 2019.
Quantum advantage, or known as the buzzword “quantum supremacy”, refers to the idea that a quantum device can solve a problem exponentially faster than a classical computer.
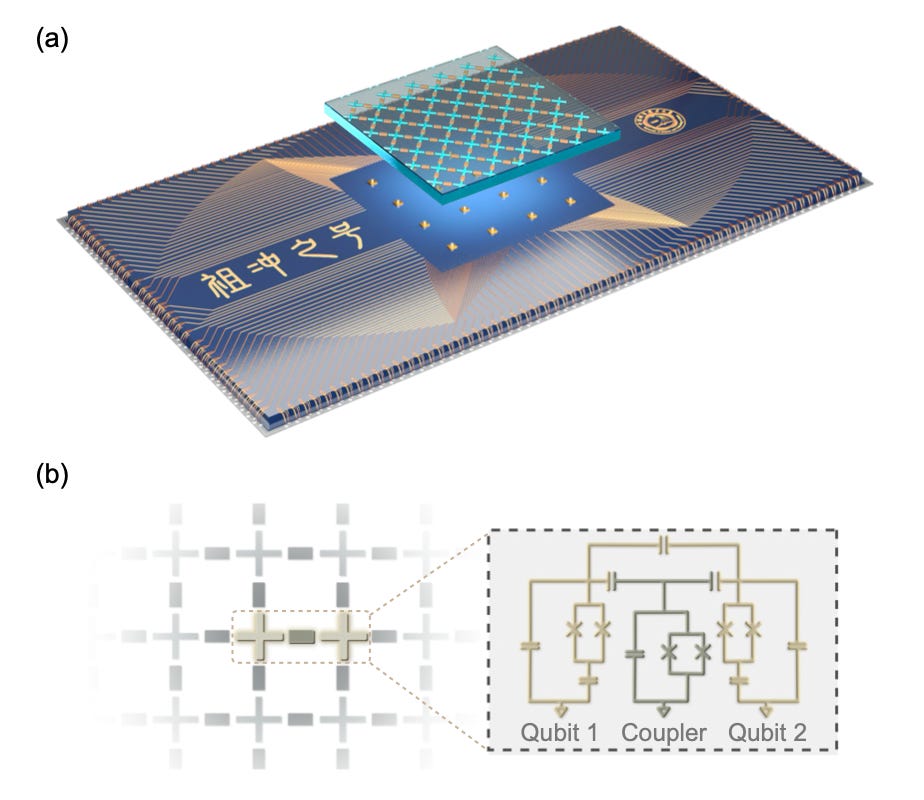
In the pre-print paper Strong quantum computational advantage using a superconducting quantum processor, the research team performed the benchmark “random quantum circuits sampling” task using a programmable 66-qubit superconducting quantum processor, named Zuchongzhi to revere this ancient Chinese astronomer, mathematician, and creator, with up to 56 qubits. They claimed the sampling task finished by Zuchongzhi in about 1.2 hours will take the most powerful supercomputer at least 8 years.
The quantum processor (shown above) consists of two sapphire chips. One carries 66 qubits and 110 couplers, and each qubit couples to four neighboring qubits except those at the boundaries. The other hosts the readout components and control lines as well as wiring. These two chips are aligned and bonded together with indium bumps.
VOLO: Transformer outperforms CNN without extra data
The introduction of Vision Transformers (ViTs) last year by Google has challenged the domination of convolutional neural networks in the field of visual recognition. However, even best ViTs couldn’t defeat CNNs without extra data provided.
Recently a research team led by Dr. Shuicheng Yan, a well-known Chinese researcher and former CTO of YITU who now serves as the Group Chief Scientist of Singapore e-commerce company Shopee, introduced a Transformer variant called VOLO, which achieves 87.1% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K classification, the first model exceeding 87% accuracy on this competitive benchmark.
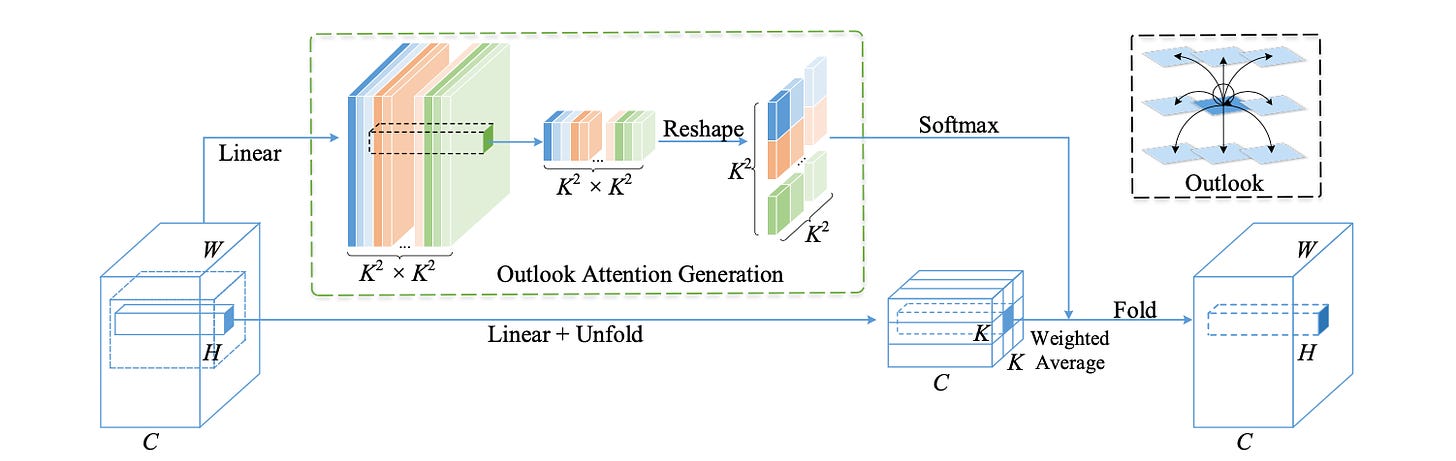
Dr. Yan’s team discovered that a major factor that limits the performance of ViTs for ImageNet classification is their low efficacy in encoding fine-level features into the token representations. To generate representations of fine-level features, they proposed Outlookers, a new simple and lightweight attention mechanism that consists of an outlook attention layer for spatial information encoding and a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) for inter-channel information interaction. Above is an illustration of the outlook attention. Researchers argued that outlook attention combines the advantages of both convolutions and self-attention.
Experiments showed that the VOLO model with 296M parameters can achieve 87.1% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet, setting a new record in case of no extra training data.
Baidu introduces uncrewed excavator system
Chinese tech giant Baidu is known for its autonomous driving tech under the brand Apollo. Now their researchers managed to extend its autonomy capability to other areas like construction.
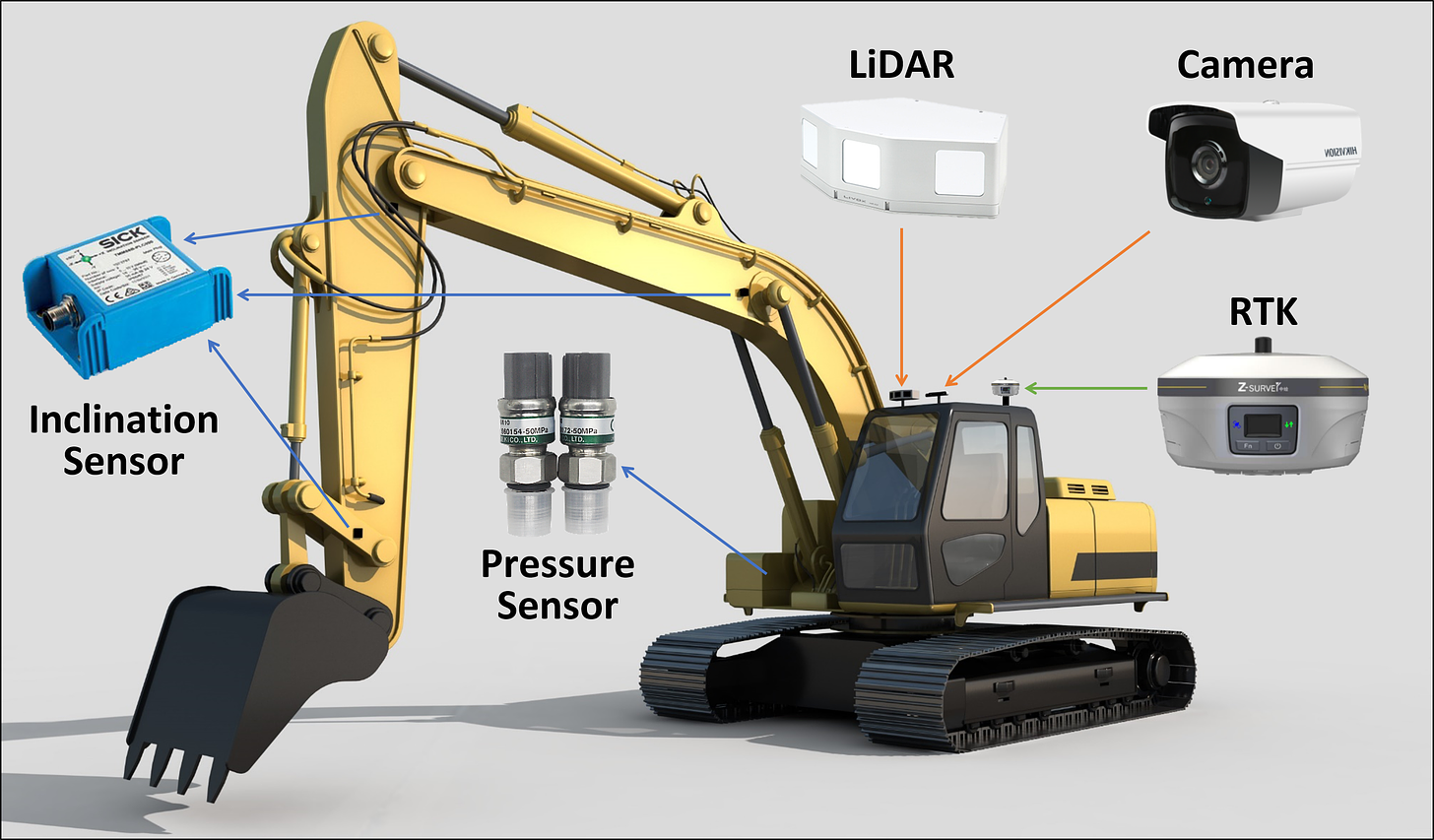
This week, researchers from Baidu and the University of Maryland introduced an autonomous excavator system (AES) that can perform a variety of real-world excavation tasks, such as handling waste or removing piles of rocks, for 24 hours without human intervention. The result was published in Science Robotics.
The motivation behind AES is hiring shortages for skilled heavy machinery operators most construction companies are facing. That’s why they are looking to create excavator robots. However, the challenge is most industrial robots are comparatively smaller and function in more predictable environments, excavator robots must be able to handle uncontrollable environments and continue running under difficult weather conditions.
The architecture of AES is quite similar to autonomous vehicles, centered with a sensor-fusion perception module connected with a prediction module and a control module. The perception adopts a so-called “coarse-to-fine” strategy to perceive the 3D environment and identity target materials. With this modular design, the AES architecture can be effectively utilized by excavators of all sizes and is suitable for diverse applications.
Baidu has been collaborating with several of the world's leading construction machinery companies, including XCMG, to automate traditional heavy construction machinery with AES, according to the company. You can find more details here.
Investment news
Merely four days after raising $4.4 billion in the IPO on Wednesday, June 30, Chinese ride-hailing giant Didi Global faced a cybersecurity review by Chinese regulators along with a halt of new registrations. On Sunday, the Chinese regulators further ordered app stores to remove the Didi Chuxing app over an alleged illegal collection of users’ personal data.
Chinese CPU designers Loongson Technology filed for an IPO on Shanghai's STAR Market, seeking to raise RMB 3.5 billion yuan (~$544 million) which will be used for R&D in chip process and high-performance graphic chips and systems. Founded in 2010, Loongson Technology has for years been developing general-purpose MIPS64 CPUs. The company recently announced it had introduced its own CPU instruction set architecture (ISA), Loongson Architecture (LoongArch). The first processors based on LoongArch have already been taped out and will be released this year.
Chinese AI unicorn YITU Tech has withdrawn from an IPO on Shanghai’s STAR Market, which was supposed to help the company raise RMB 7.5 billion yuan (~$1.16 billion). YITU filed a Chinese Depositary Receipt offering on Shanghai's STAR board in November, but then applied to terminate its IPO application on March 11. The company resumed its IPO approval process in June but soon applied for IPO termination. Founded in 2012, YITU provides AI solutions along with high-performance computing power in smart city, healthcare, and intelligent business.