Alibaba's ChatGPT; Build LLMs with LMFLOW; HuggingGPT Connects HuggingFace Models with ChatGPT
Weekly China AI News from Mar 27 to April 9
Dear readers! In this week’s edition, we’ll delve into Alibaba’s surprising early reveal of its ChatGPT-like model, Tongyi Qianwen. We’ll also explore HKUST’s open-source framework designed to help developers in fine-tuning LLMs, and introduce HuggingGPT, an innovative framework that connects 400+ HuggingFace models with ChatGPT.
Weekly News Roundup
Alibaba Cloud Releases its ChatGPT For Selective Testing
What’s new: Last Friday, Alibaba Cloud unexpectedly unveiled its ChatGPT-like large AI model, called “Tongyi Qianwen” (通义千问). The model is currently open for invited testing by enterprise clients. Here’s what we know so far:
Like ChatGPT and Baidu’s ERNIE Bot, Tongyi Qianwen understands language prompts and responds through language generation in a dialogue interface. It can write literary fiction, generate code, and express opinions, up to a maximum of 1,000 words.
Alibaba Cloud states that Tongyi Qianwen can communicate in Chinese, English, Japanese, and several other languages.
Developed by Damo Academy, Alibaba’s research division, Tongyi Qianwen is built on Alibaba’s home-grown models. The company has been working on large language models since 2019, including StructBERT and PLUG (Pre-training for Language Understanding and Generation), a 27B-parameter Chinese language model.
Tongyi Qianwen does not yet support multi-modal understanding or generation.
A “Treasure Chest” toolbox is included with Tongyi Qianwen, featuring text generation functions for specific tasks, such as creating outlines, SWOT analyses, and poetry in various domains.
Alibaba Cloud’s CTO, Jingren Zhou, stated that Tongyi Qianwen will serve as the foundation for Model-as-a-Service.
More details about Tongyi Qianwen will be disclosed at the Alibaba Cloud event on April 11.
HKUST Open Sources LMFLOW to Build LLMs for All
What’s new: The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology has open-sourced LMFLOW, a toolbox for fine-tuning large AI models. With LMFLOW, developers can train a 7B-parameter LLaMA using just one 3090 GPU in 5 hours, creating a personalized model.
Vision: According to the authors, the code repository is more than a simple model, encompassing the entire training workflow, model optimization, and testing tools. It enables developers to construct various language models, including conversational, question-answering, and text-generation models, among others.
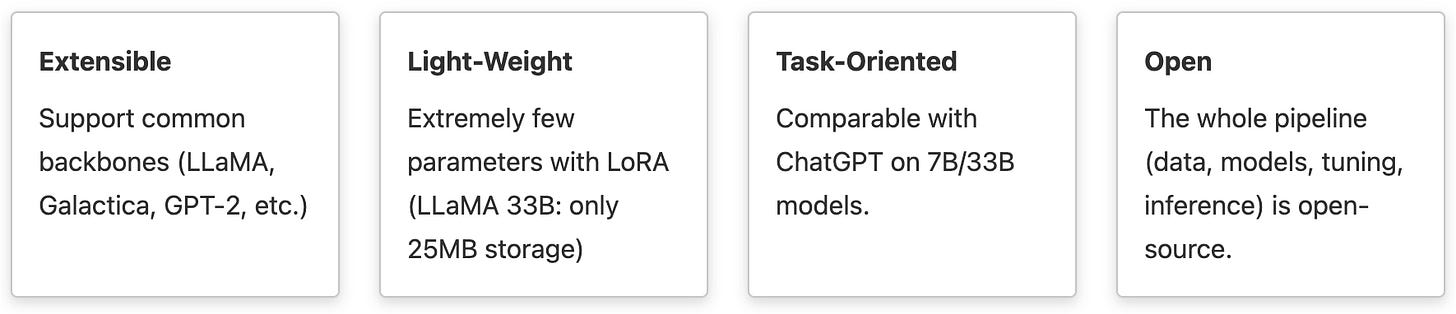
Features: LMFLOW boasts four key attributes: extensibility, lightweight design, task orientation, and openness.
The code repository currently includes four fine-tuned and four medical LLaMA models, ranging from 7 billion to 33 billion parameters. It provides essential pipelines for training LLMs, such as task tuning, instruction tuning, parameter-efficient tuning, large model inference, and alignment tuning. LMFLOW supports all decoder models in HuggingFace, as well as LLaMA, GPT2, GPT-Neo, and Galactica.
Introducing HuggingGPT: Using ChatGPT to Control HuggingFace Models
What’s new: Researchers from Zhejiang University and Microsoft Research Asia proposed HuggingGPT, a framework that leverages LLMs (e.g., ChatGPT) to connect various AI models in machine learning communities (e.g., Hugging Face) to solve AI tasks.
Why it matters: Despite the early success of LLMs like ChatGPT, these models still face considerable challenges in processing multimodal inputs, such as visual and speech data, effectively handling complex real-world tasks, and matching the expertise of specialized expert systems. Researchers propose that LLMs should be capable of coordinating with external models to fully harness their capabilities.
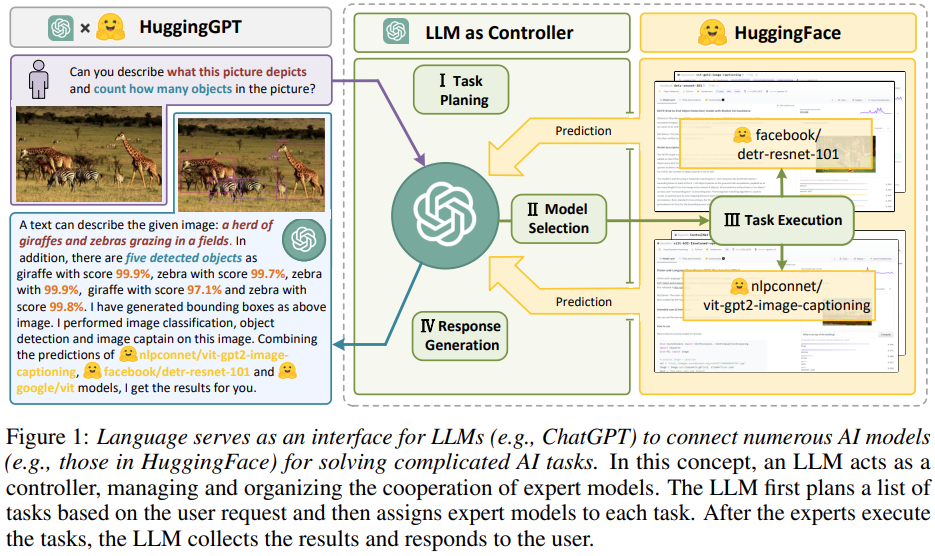
How it works: In the HuggingGPT framework, ChatGPT acts as the brain to assign different tasks to HuggingFace’s 400+ task-specific models. The whole process involves task planning, model selection, task execution, and response generation.
Task planning: LLM parses user requests into a task list and determines the execution order and resource dependencies among tasks.
Model selection: LLM assigns appropriate models to tasks based on the description of expert models on Hugging Face.
Task execution: Expert models on hybrid endpoints execute the assigned tasks based on task order and dependencies.
Response generation: LLM integrates the inference results of experts and generates a summary of workflow logs to respond to the user.
Results: Researchers tested HuggingGPT on a wide range of multimodal tasks, showing its capabilities in various forms of tasks such as detection, generation, classification, and question-answering. In complex tasks, HuggingGPT was able to cope with multi-round conversation scenarios, expand simple requests into multiple related tasks, and accommodate user requirements by organizing multiple expert models to cooperate in parallel.
What Else Do You Need to Know?
📈 SenseTime shares surged 13%, the most in two months, amid rumors that the company is preparing to launch a competitor to the AI phenomenon ChatGPT.
👀 DJI unveiled a new generation of L2+ ADAS solutions, with merely 32 TOPS of computing power and 7V/9V visual sensors. The system operates without high-precision maps or LIDARs.
🔰 360 announced that its AI product “360 Smart Brain (360智脑),” developed based on the 360GPT large models, has been employed in search and will be open for testing to enterprise users.
🔊 iFlytek’s “1+N Cognitive Intelligence Large Model” will debut on May 6. The “1” represents the general cognitive intelligence large model and a high-efficiency training platform, while the “N” refers to specialized large models designed for multiple industry sectors.
💊 The Ministry of Science and Technology, in collaboration with the National Natural Science Foundation, has recently launched the “AI for Science” project. This initiative will focus on research needs in crucial areas like drug development, gene research, bio-breeding, and new materials development.
🤖 Intellifusion, a Shenzhen-based AI vision processor company, surged 189% in its Shanghai IPO debut, valued at RMB 45.1 billion at its peak.
🚀 Xiaochuan Wang, Sogou's founder and ex-CEO, has established Baichuan Intelligence (百川智能) to develop China’s answer to OpenAI. With $50 million in funding and a 50-member team, their goal is to launch China’s best LLM by year’s end.
Trending Research
FengWu: Pushing the Skillful Global Medium-range Weather Forecast beyond 10 Days Lead
Affiliations: Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, The Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Meteorological Bureau
FengWu is an AI-based global medium-range weather forecast system using a multi-modal, multi-task approach with a deep learning architecture. It outperforms DeepMind’s GraphCast in 80% of predictands and extends the skillful global medium-range weather forecast to 10.75 days lead, marking a significant improvement in forecast skill.
Hierarchical graph learning for protein–protein interaction (Nature Communications)
Affiliations: Tencent AI Lab
HIGH-PPI is a hierarchical graph learning model that predicts protein-protein interactions (PPIs) with high accuracy. The model incorporates both outside-of-protein and inside-of-protein views, offering a robust, domain-knowledge-driven framework for PPI prediction and interpretation.
How well do Large Language Models perform in Arithmetic tasks
Affiliations: Alibaba Group, Tsinghua University
This work introduces MATH 401, an arithmetic dataset designed to evaluate the arithmetic abilities of large language models, including GPT-4, ChatGPT, InstrctGPT, Galactica, and LLaMA. MATH 401 tests these models with various arithmetic expressions and provides a detailed analysis of their capabilities. The dataset and evaluation codes are available at https://github.com/GanjinZero/math401-llm.
Better Aligning Text-to-Image Models with Human Preference
Affiliations: Chinese University of Hong Kong, SenseTime Research, Qing Yuan Research Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Centre for Perceptual and Interactive Intelligence (CPII)
The study addresses the misalignment of text-to-image models with human aesthetic preferences by developing a Human Preference Score (HPS). Using this score, they adapt the Stable Diffusion model to generate images better aligned with human preferences. Project page: https://tgxs002.github.io/alignsdweb/.