AI Streams for 100 Days; Google's Shanghai Veterans Start New Venture; Memory-Less Simulation With QuanTaichi
China’s AI news in the week of July 13, 2021
Would you like to subscribe here to support Recode China AI?
Microsoft’s Chinese AI spinoff Xiaoice unveils ‘Supernatural Voicetech’
Last year, Twitch personality GPHustla broke the human record for the most extended stream hours by reaching over 1,000 hours nonstop. Guess what? It’s a piece of cake for AI.
Two AI avatars (AI周小豆 and AI201) developed by Xiaoice, a China-based Microsoft spin-off specialized in chatbot technology, have been conversing with each other for 93 days, 2232 hours, and it’s still counting.
The live stream is part of a technology publicity campaign to reflect Xiaoice’s new ‘Supernatural Voicetech,’ which is touted to be the first technology that elevates fabricated speech to a level almost indistinguishable from authentic human voices. In addition, Xiaoice has made its “Avatar framework” APIs available so that third-party developers can tap it into their AI customization - virtual streamers, customer service agents, or digital companions.
To enable a fully interactive chatbot system, Xiaoice includes advanced speech synthesis and NLP techniques like full-duplex voice tech for long-term voice interaction, multimodal models that incorporate voice and vision inputs, and a dialogue engine fourth-gen deep neural net that generates music.
Founded in 2014 by a Microsoft team, Xiaoice now has 660 million users globally and provides its technology to business customers in finance, retail, automobile, and real estate.
The company has recently bagged more than RMB 500 million yuan ($77 million) in a Series A funding led by Hillhouse Capital Management, reaching a valuation of $1 billion.
Alphabet’s Verily Veterans Reboot AI Health Business in China After Exit
In 2019, Alphabet planned a comeback in China with a push into artificial intelligence and life sciences. Its healthcare spin-off Verily set up a Shanghai office and hired about 70 people. However, Verily China received a setback after struggling to make inroads on a critical health-mapping project named Baseline Project. As a result, the company shut its Shanghai office in 2020 and shifted major Asia affairs to its Singapore office.
The story isn’t over yet. Dozens of Verily China’s veterans, led by former Verify China General Manager Xiao Chen (陈晓) and Chief System Architect Pengcheng Xu (徐鹏程), rebooted AI health business under a new company named Aurora, or Yaocheng (耀乘), in August 2020. The company announced a seed financing round of tens of millions of yuan led by Lightspeed China and Hankang Biotech Fund in January 2021. The company has recently raised over 100 million in new funding round, Chinese media QbitAI reported.
According to the company, Aurora’s vision is to accelerate the research and development of life sciences and build a comprehensive SaaS platform. Its main product, AuroraPrime clinical data management platform, provides one-stop services from data collection to conversion.
QuanTaichi: A Compiler for Quantized Simulations
Thanks to increasing computing power and improving computational graphic technology, high-resolution simulation is widely utilized for various industrial applications in sectors like movie production, climate change, life sciences, and physics simulation. However, storing details of high-resolution simulation demands a tremendous amount of memory, especially on GPUs.
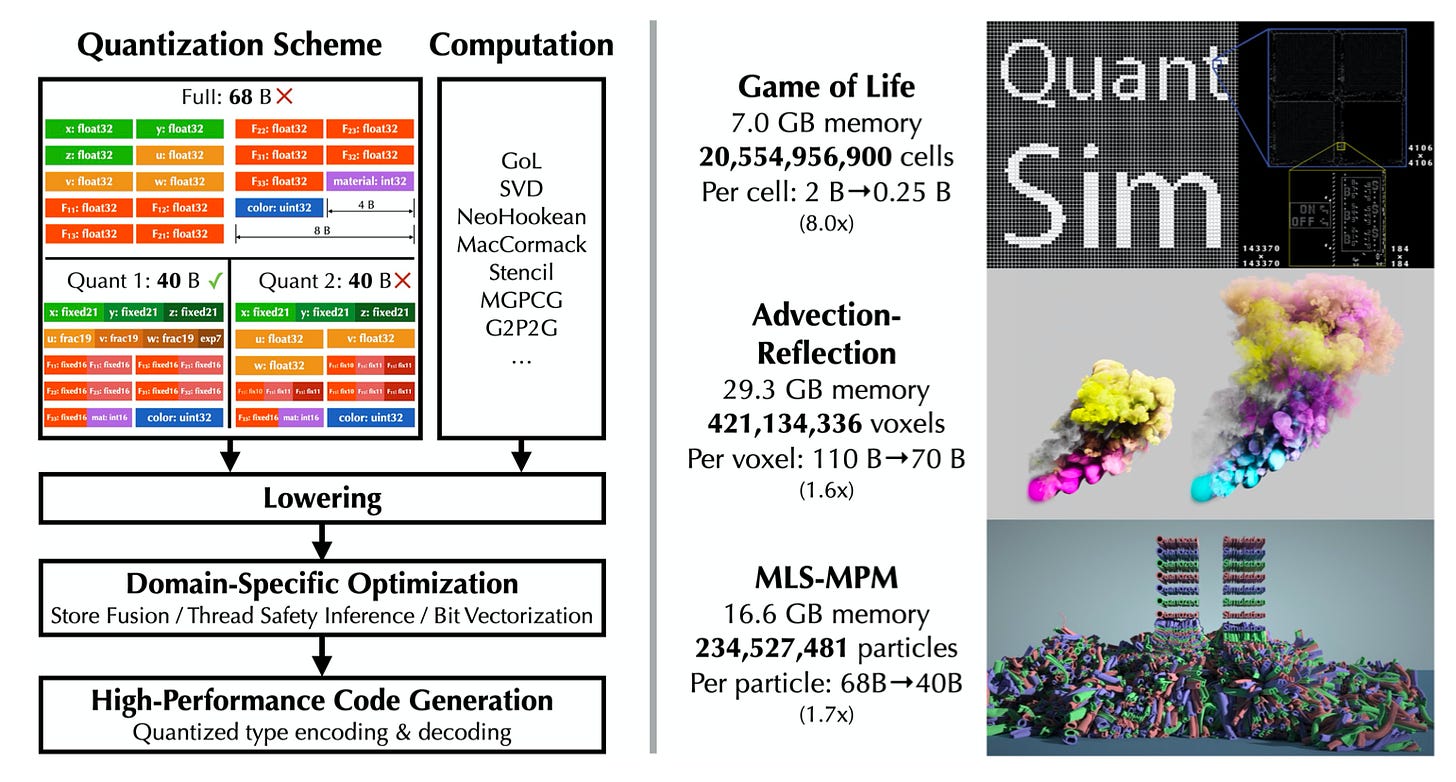
Recently a team of researchers from MIT, Tsinghua University, Zhejiang University, and TikTok’s China rival Kuaishou introduced QuanTaichi, a compiler for high-performance physical simulation with significantly reduced memory costs. In addition, using QuanTaichi, low-precision or quantized numerical data types can be used and packed to represent simulation states, further reducing memory utilization. The paper has been accepted in SIGGRAPH 2021.
QuanTaichi builds on Taichi, a data-oriented programming language designed for high-performance computer graphics proposed in 2019. The project has been open-sourced in part of Taichi on GitHub.
With one GPU, researchers can simulate a Game of Life with 20 billion cells (8× compression per pixel), an Eulerian fluid system with 421 million active voxels (1.6× compression per voxel), and a hybrid Eulerian-Lagrangian elastic object simulation with 235 million particles (1.7× compression per particle).
Taichi has helped create multiple visual effects on the Kuaishou platform, such as liquid and smoke effects, making high-resolution simulation possible on even entry-level mobile devices.
Investment News
China’s e-commerce giants for life services Meituan has lately made a surprising investment moving by pouring money into AI semiconductor company Zhiaixin Semiconductor (智砹芯半导体), joined by GGV Jiyuan Capital, Tianchuang Capital, Yaotu Capital, and Jubaichuan. Founded in April 2020, the company hasn’t publicly shared any products or technological progress but has already bagged RMB hundreds of millions yuan in a Series B funding.
Kingsware (金智维), a Shenzhen-based robotic process automation (RPA) startup, has recently raised RMB 200 million yuan in a Series B funding led by GLVentures. Founded in 2016, Kingsware offers RPA software for over 400 clients across sectors like finance, insurance, real estate, and healthcare, automating repetitive tasks and optimizing business operations.
Inspir.ai, a Beijing-based AI startup, has raised RMB 300 million yuan in a Series A funding led by GGV Capital. The company was founded in 2017 by Alibaba veterans aiming to create the ultimate agent with general intelligence. Current offerings are mainly AI platforms and solutions that can help gaming companies build in-game virtual characters.